Lean Product Development? The Key to Digital Product Management Success
Lean product development is a way of developing products and services that maximise customer value while minimising waste. However, many struggle with lean product development flow, processes, and applications, hindering organisational growth and customer satisfaction.
Are you facing challenges implementing LPD principles within your project or organisation? This article will not only provide a clear understanding of LPD but also offer actionable solutions to overcome its challenges. Embrace LPD to enhance your product management practises and better serve your customers.
Table of Contents
- What is Lean Product Development?
- The principles of Lean Product development (LPD)
- Benefits of Lean Product Development
- Applicability of Lean Product Development Principles
- Challenges and limitations of Lean Development Process
- Conclusion
- Machine Learning In Finance: 12 Essential Applications
- How To Create Interactive Compliance Training For Bank Employees
- How Fintech Apps Are Using Gamification To Increase User Engagement
- Top Gamification Companies for Employee & Customer Engagement
What is Lean Product Development?
Lean Product Development (LPD), a concept focusing on efficient product and service creation, strives to meet customer demands effectively. LPD principles are rooted in the Toyota Product Development System, known for its innovative, efficient product development approach. LPD applies the concepts of lean manufacturing and methods of thinking to the product development process, such as:
- Defining value from the customer’s perspective.
- Identifying and eliminating activities that do not add value.
- Optimising the flow of work and information.
- Responding to customer demand and feedback.
- Pursuing continuous improvement and learning.
The role of lean in product development is to assist product managers and teams in creating products and services that solve real problems for real customers. It also aims to reduce costs, risks, and time to market. Additionally, LPD fosters a culture of innovation and collaboration within the organisation. This involves everyone collaborating to create value for customers.
The principles of Lean Product development (LPD)
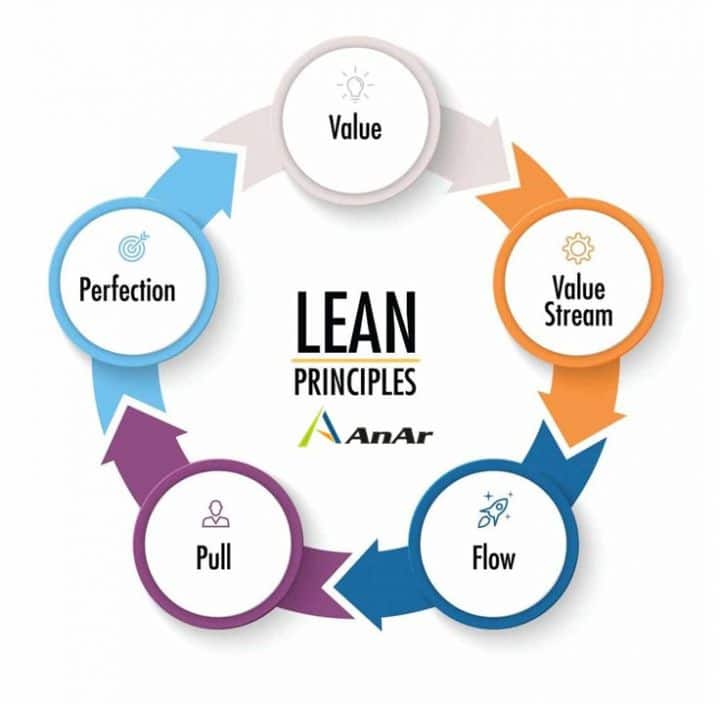
Source: AnAr Solutions
Lean development is based on six core principles that guide the product development process. These principles are:
#1. Specify a value for your customers
Lean Product Development begins with a clear understanding of what customers truly value. It’s about identifying their needs and desires and ensuring every effort aligns with these priorities.
You can use various methods to gather customer insights, such as interviews, surveys, observations, or experiments. Tools like personas, customer journeys, or value proposition canvasses help define customer segments, focus groups, and their value propositions. They are beneficial in this process.
#2. Identify and focus on your value stream
Success in the digital product realm hinges on recognising and enhancing the value creation stream. By pinpointing every step of the product development cycle and refining it, you create a seamless flow that caters to customer demands.
To map your value stream’s current state, identify waste and inefficiency using tools like value stream mapping or Gemba walks. Afterwards, design your future state with improved flow and quality.
#3. Create flow by eliminating waste
Waste is the nemesis of efficiency. LDP seeks to eliminate waste in all forms, whether unnecessary processes, excess resources, or redundant tasks. Waste can be classified into eight types: defects, overproduction, waiting, non-utilized talent, transportation, inventory, motion, and extra-processing.
You can use 5S, Kanban boards, or visual management tools to eliminate waste and create flow in your value stream. The 5S tool is particularly effective in maintaining an organised and efficient workspace.
#4. Respond to customer’s pull
Instead of pushing products onto the market, LDP draws inspiration and direction from customer demands. It’s a responsive approach that tailors products to meet genuine needs.
Implementing pull in your value stream requires aligning production with customer demand. Utilise pull systems, takt time, or heijunka for this purpose. Additionally, gather customer feedback and integrate it using feedback loops or A/B testing.
#5. Pursue perfection through repetition
Continuous improvement is at the core of Lean Product Development. It encourages iterating and refining processes to attain perfection over time.
Perfection is attainable through repetition. Apply the cycle of plan-do-check-act (PDCA) or build-measure-learn (BML) to all aspects of your product development process. Repetition facilitates learning from mistakes, process improvement, and validation with real customers.
#6. Put people first
Lean recognises that the people involved in lean company and product development are the key to success. Empowering employees, giving them autonomy, and respecting their expertise fosters a culture of innovation and commitment.
Consider tools like team huddles, retrospectives, and gamification to cultivate a culture of innovation and collaboration within your organisation. You must also provide your people with training and coaching to develop their skills, knowledge bases, and competencies.
These principles form a solid foundation for Lean Product Development, enabling organisations to create efficient, customer-aligned, and high-quality products.
Benefits of Lean Product Development
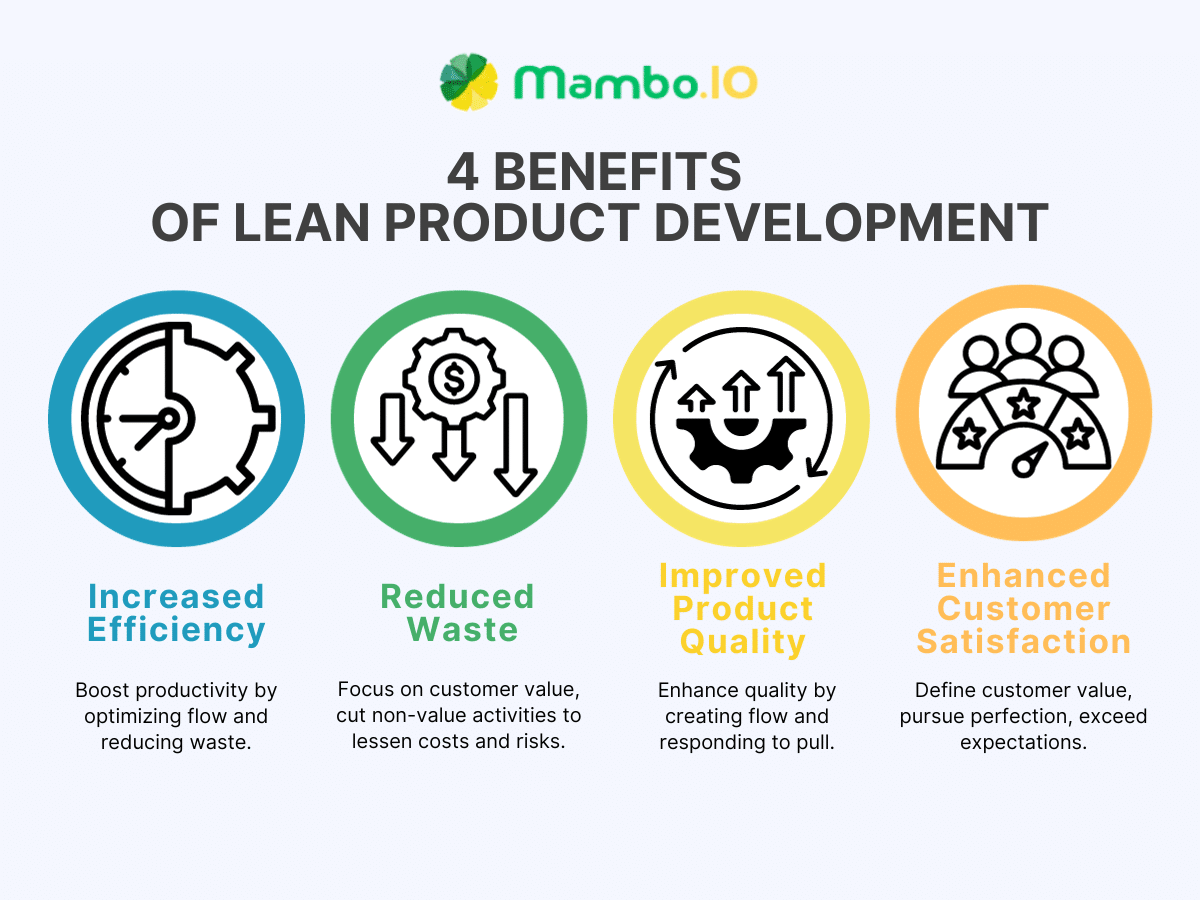
Lean product development offers many benefits for product managers and teams that adopt it as their working method. Some of these benefits are:
#1. Increased efficiency
Reduce waste and optimise flow in your value stream to increase productivity. This reduces cycle time and delivers more value with fewer resources.
Example: Spotify, a leading music streaming service, implemented Lean practices in its software development process, like A/B testing and MVPs. By streamlining its product development pipeline and eliminating bottlenecks. Spotify reduced its release cycle from weeks to days, allowing it to deliver new features and updates more efficiently.
#2. Reduced waste
Focus on customer value and eliminate non-value-adding activities. This reduces costs and risks and minimises the environmental impact.
Example: Adobe, a prominent software company, adopted the Lean method in its product development. By focusing on customer value and improving collaborative work, Adobe improved resource allocation and enhanced overall product quality.
#3. Improved product quality
Create flow and respond to customer pull in your value stream to improve product quality. This approach helps prevent defects, errors, and rework, enhancing the overall quality.
Example: Microsoft’s Windows development team embraced the Lean process to respond more effectively to customer journeys and feedback. This shift led to a significant reduction in software bugs and crashes. It resulted in a more stable and higher-quality operating system.
#4. Enhanced customer satisfaction
Specify a value for your customers and pursue perfection through repetition in your value stream. Enhance and maximise customer satisfaction by delivering products and services that solve their problems and exceed expectations.
Example: Dropbox, a cloud storage and file-sharing service, integrated Lean development into its product work and processes. They consistently deliver user-requested features and improve the user experience. Dropbox achieved an increase in customer satisfaction scores and a boost in user retention rates.
Applicability of Lean Product Development Principles
Lean Product Development isn’t limited to specific industries. Its versatile framework can be applied to projects across various sectors, including healthcare, manufacturing, and software development.
Lean in software development
In software, lean principles find embodiment in Agile methodologies, DevOps practises, and User-Centric Design. These prioritise speed, flexibility, and maximising customer feedback. Here’s how Lean thinking plays out in the digital arena:
Agile methodologies: Agile frameworks like Scrum and Kanban emphasise customer needs, iterative development, and cross-functional team collaboration. This leads to shorter development cycles and a sharper focus on value delivery.
Source: 360logica
Continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD): CI/CD pipelines automate the testing, integration, and deployment of code, minimising manual intervention and accelerating the release process. This aligns with the emphasis of the Lean methodology on eliminating waste and achieving a streamlined workflow.
User-centric design: Lean Product Development promotes empathy for end-users. In the digital space, this translates to user-centric design, crafting products with a deep understanding of user needs, preferences, and pain points.
Lean in digital product management
Digital product managers stand to gain substantially from Lean principles. By applying Lean Product Development principles, they can:
Gain rapid feedback: Lean encourages the frequent release of Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) to obtain early feedback from users. This feedback loop helps refine the product continuously, resulting in a better user experience.
Optimise resource allocation: Digital product managers can use Lean principles for efficient resource allocation. This ensures only necessary features are developed, minimising unnecessary work and saving resources.
Boost customer satisfaction: Lean’s focus on delivering value directly aligns with customer satisfaction. By concentrating on features and improvements that customers truly care about, digital products become more successful and beloved.
Lean development beyond software
Lean Product Development’s principles aren’t confined solely to software. Various industries, from healthcare to manufacturing, have implemented Lean methodologies. It drives efficiency by reducing waste and enhancing product quality. While the core principles remain the same, the application is tailored to each industry’s needs.
Challenges and limitations of Lean Development Process
As promising as LDP is, it’s not without its challenges:
-
Resistance to change
Implementing Lean principles can face resistance from teams accustomed to traditional development cycles. Convincing stakeholders to embrace change can take time and effort.
To overcome this resistance, communicate the benefits and vision of LPD clearly and consistently. Involve your people in the change process, providing training and coaching to develop their skills.
-
Limited applicability to certain industries
While versatile, LDP may be a variety of solutions. Some industries may require specific processes that don’t align with Lean principles. Some industries may have strict regulatory requirements, intellectual property rights, or safety standards, limiting LPD’s flexibility and experimentation.
In these cases, you must adapt and customise LPD to fit your specific context and situation.
Conclusion
Lean Product Development holds the key to transforming digital product management. Software companies can thrive in a competitive market by aligning with customer needs, eliminating waste, and embracing continuous improvement.
The implications for future research and digital practice are immense, promising innovation and growth.
Explore our offers and embark on your Lean Product Development journey today! Embrace efficiency, enhance quality, and revolutionise your digital products with Lean principles.
At Mambo, we’re committed to empowering product managers and software companies with the tools they need to excel. Learn how to take your business to the next level with gamified activities that align with your goals. Check out Mambo today!
Download your free
“Gamification Guide”
Get your PDF now and start transforming your approach to digital engagement!
Latest Posts
Machine Learning In Finance: 12 Essential Applications
The impact of machine learning on finance is significant. Thanks to this technology, financial institutions are now equipped to make efficient decisions. Through the analysis of data sets, machine learning […]
How To Create Interactive Compliance Training For Bank Employees
Banking compliance training isn’t just another task. It’s the stage where everything else performs. Banks must navigate a myriad of regulations and laws. After all, this is a trust-driven, high-stakes […]
How Fintech Apps Are Using Gamification To Increase User Engagement
Discover how gamification in fintech is revolutionizing financial engagement, making banking fun & boosting user loyalty.





