Ultimate Guide To Product Design And Development
Product design and development are twin imperatives for bringing any product to life.
The difference between product design and development relies on the process. One focuses on design and functionality, while the other focuses on product launch.
Product design and development are paramount in every industry.
Product development oversees the product life cycle. It begins with market analysis and planning and ends with the launch. Product design is where planning, creation, and design converge in the development cycle.
This article will focus on understanding product design and development, its processes, characteristics, and main differences.
Table of Contents
- What comprises the product design and development team?
- What is product design?
- Stages of product design
- Characteristics of a successful product design
- What is product development?
- Stages of product development
- Characteristics of a successful product development
- Product design VS product development
- Conclusion
- Machine Learning In Finance: 12 Essential Applications
- How To Create Interactive Compliance Training For Bank Employees
- How Fintech Apps Are Using Gamification To Increase User Engagement
- Top Gamification Companies for Employee & Customer Engagement
What comprises the product design and development team?
Product design team
Defining the process of every team member involved in product design and development is important in understanding the whole process.
The team responsible for product design includes UX designers, UX researchers, and UI designers. The UX designers build product prototypes and collaborate with UX researchers to brainstorm and define product structures and flows. UI designers are responsible for delivering aesthetically pleasing and seamless product design.
Product development team
On the other hand, the product development team comprises the product manager, UX researchers, analytics, and marketing. This team collaborates consistently to create the product development strategy and implement it. Their roles include:
- Product manager – Managers are responsible for creating a vision of how the final product will turn out. They are in charge of developing and implementing a strategy.
- UX researchers – They monitor and analyse how users engage with the product and do the research to test usability.
- Analytics – They research market trends and understand what the users want. They are the deciding factors on how the final product will be developed.
- Marketing – Product marketers decide the target market for the product. They are in charge of planning the product launch and the positioning of the product.
Both teams responsible for product design and development are important in ensuring product success.
What is product design?
Source: miroslavo
Product design is the process of conceiving an idea for a product and refining it to meet specific market standards. It focuses on solving user problems and addressing the needs of the market.
Product design involves crafting a product, encompassing aesthetics, functionality, usability, and ergonomics. Regardless of the product design you envision, the process comprises essential stages we’ll cover later.
A successful product design understands the needs of the end users and can be measured by how flawless the execution is. When the product can anticipate user needs based on usage, that can be considered a good product design.
But it doesn’t end there. Good product design practices must be applied throughout the product lifecycle. Product design is vital in constantly improving user experience, from idea generation to prototyping and usability to testing.
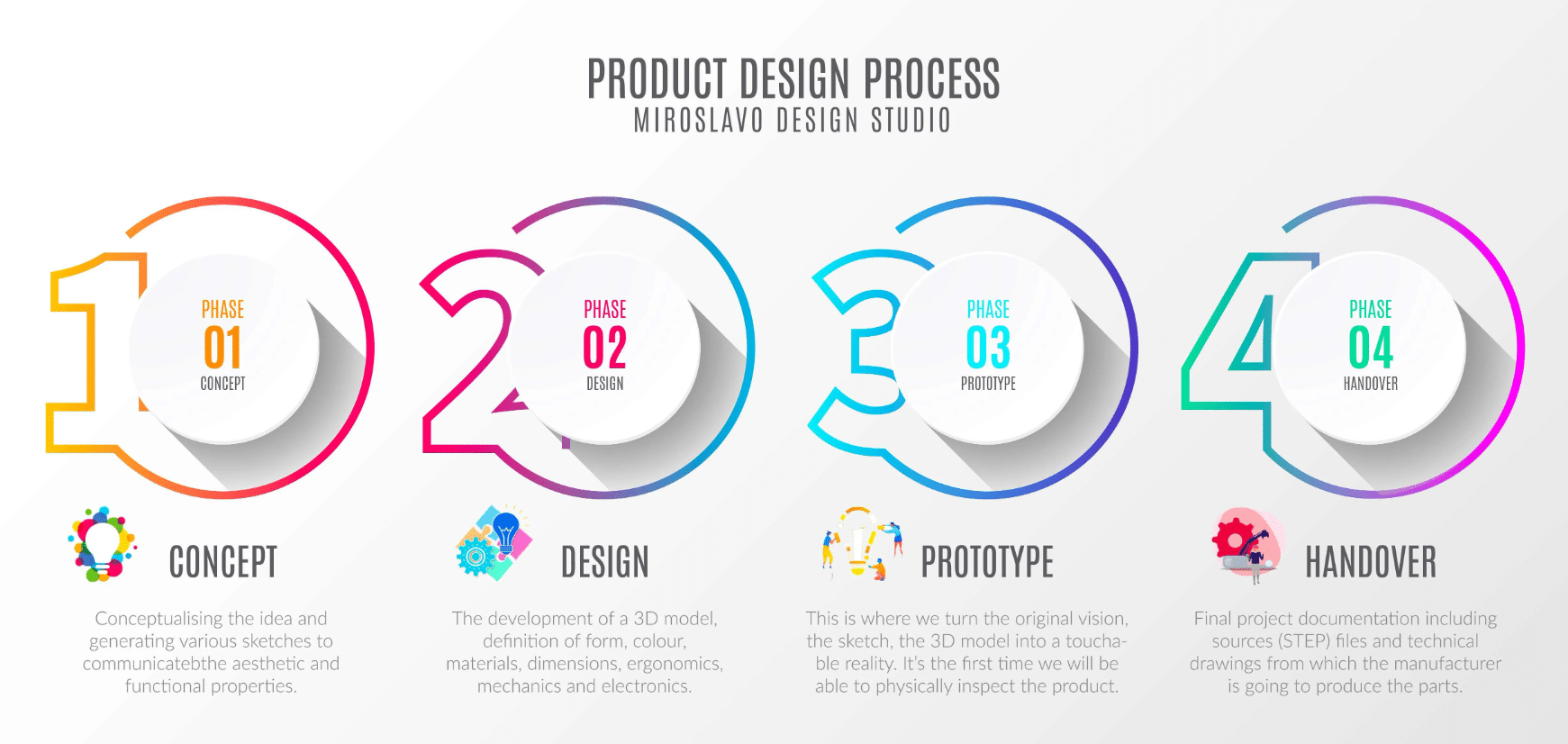
Stages of product design
#1. Ideation
Product managers brainstorm innovative concepts for crafting a new product during this journey. General ideas originate from product teams and the reverse engineering team.
Consumer feedback, market analysis, and competitor reviews provide input in the feedback collection. During this stage, designers conceive ideas. Internal and external sources contribute to this.
Internal sources include employee feedback, market analysis, R&D, and reverse engineering. External sources include customer feedback, market trends, and benchmarking. A comparison with the best product in the market is integral to this process.
#2. Feasibility analysis
Feasibility analysis considers market, cost, tech, and risk for the product design. After research and approval, the process will proceed to product design.
Here, product managers will engage in the following feasibility studies:
- Market
- Economic
- Technical
- Strategic
- Product risk analysis
Afterwards, the performance specifications are set for the particular product concept. If the feasibility study goes well, development approval may follow.
#3. Product prototype
In this stage, product designers convert performance specifications into technical requirements. After evaluating its performance, the designer revises and retests the design.
The transformation of performance specs to technical specs leads to preliminary industrial design. The UI, UX, and performance are then tested. The plan will be modified as the designer revises it.
#4. Testing
The prototypes undergo testing among the target market. By gathering their feedback, the final product design becomes ready for launch.
Iterative testing plays a crucial role in finalising the prototype. Actual market settings serve as the testing ground for the prototype. This is a must-do to gather feedback from the desired customer group.
#5. Product launch
At the grand finale of the product launch, the entire team collaborates as one. The marketing team focuses on reaching the right audience through strategic planning. The finance team works on the product launch budget, addressing profit and loss.
After finalising everything, the product is ready for launch to the target customers. The management, marketing, and production teams collaborate throughout this phase.
Characteristics of a successful product design
There are several characteristics to look for in a successful product design. Product managers and designers must keep the following factors when designing a product.
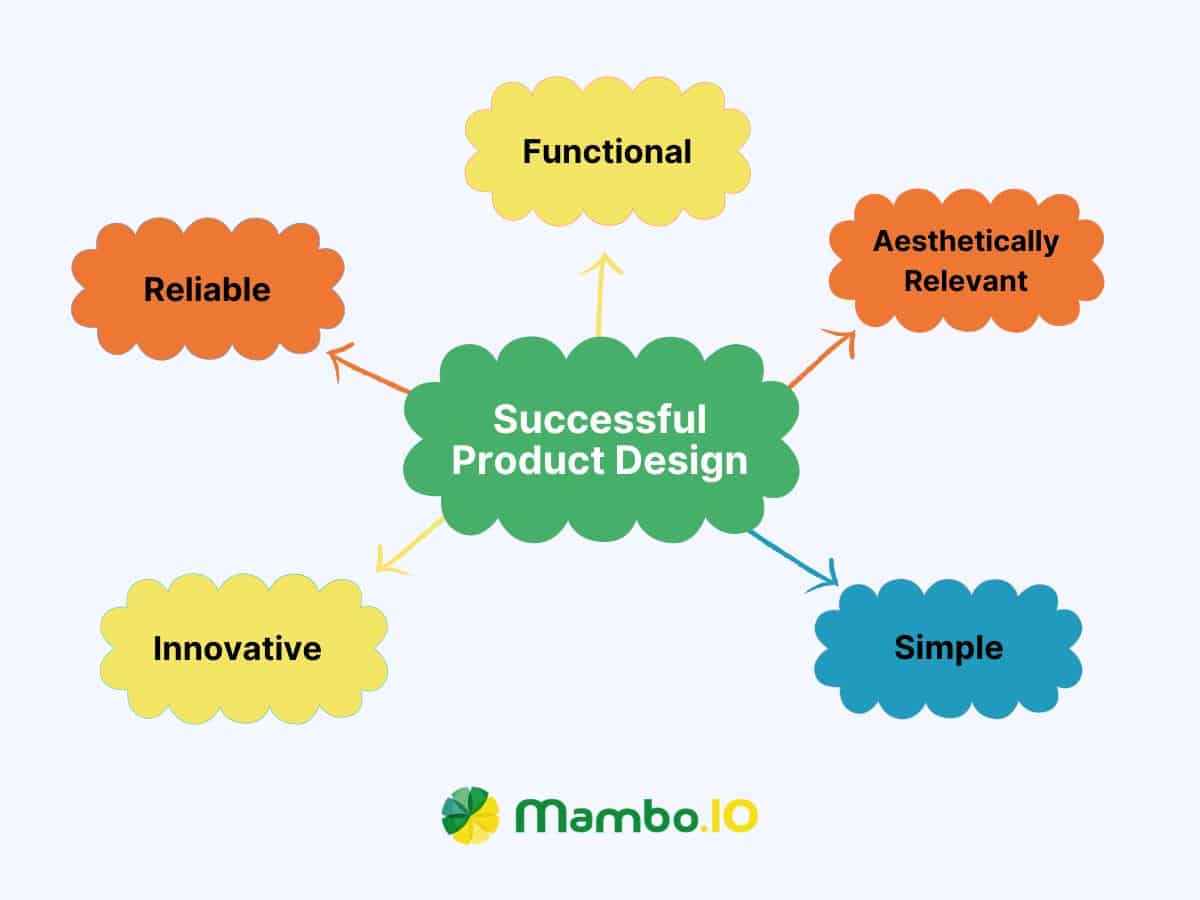
- Functional – When users choose a product, functionality and usefulness is what they have in mind. A successful product design ensures market adoption and functionality. Digital products must be designed to benefit the users and provide value to their lives.
- Aesthetically relevant – While value is essential in product design, aesthetics also plays an important role. Users opt for products that are aesthetically pleasing and easy on the eyes. If you’re a designer who wants to improve your product constantly, remember to enhance its appearance.
- Simple – Simplicity is vital in how users will see your product. Keeping it simple and functional while showing aesthetic ability is something every product designer needs to master.
- Innovative – A successful product design must bring something new and effective that will capture the attention of your target audience. Focus on the needs of your end users, your business goals, and the available technology to design an innovative product.
- Reliable – A successful product design ensures that the product is reliable and will work efficiently for a long time.
What is product development?
Source: tatvasoft
Product development involves many stages, from idea generation to product maintenance.
A collaborative effort among various teams ensures successful product development. The goal is to develop a product that meets the market’s wants and needs.
Product development necessitates assessment, cost analysis, lifecycle management, and usability studies. These factors are crucial for product success.
For successful product development, you need a clear roadmap, an active product manager, and effective product execution. You will have a favourable outcome by understanding how to incorporate these elements into your process.
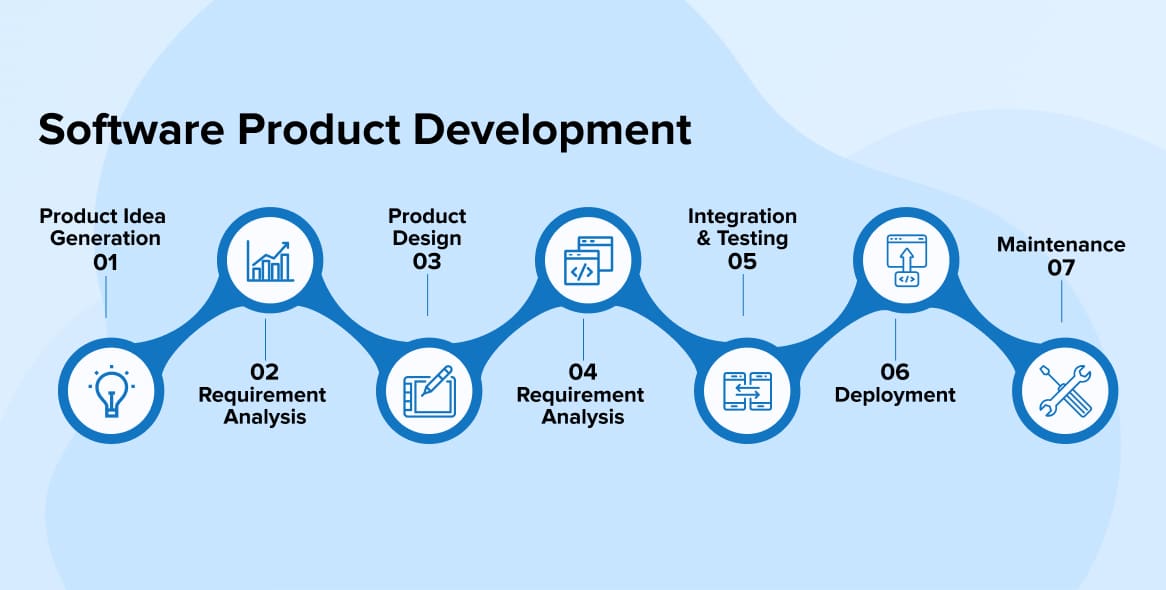
Stages of product development
#1. Idea generation
Idea generation and screening are vital for any organisation. The ideation team picks ideas from employees. These ideas are then passed to the research and development team for development.
Idea analysis and filtering occur alongside the research and development team. The product team selects a great idea that satisfies customer demand and boosts profits.
This phase is about searching for fresh and great ideas for a product. In most organisations, they have an ideation team that fosters idea development.
Development of these ideas may also fall under the R&D team’s purview. External sources, including distributors and suppliers, can contribute too. In most instances, these are required to align with client demands.
In this stage, idea analysis and filtering occur. Product developers keep the most excellent ones and discard the others.
#2. Concept development
At this stage, the product team turns their chosen ideas into concepts. This is where the marketer develops alternative product concepts based on innovative ideas. Every organisation compares feasible options that cater to customer needs.
The company takes the selected idea and turns it into a concept. The marketer generates alternative product concepts using the new concept as a foundation. Then, the company examines various options, observing if these alternatives satisfy customer demands.
#3. Business analysis
Officials examine product sales, profit, and costs at this stage. In doing so, they can understand the product’s commercial feasibility. Furthermore, catering to user demands requires market surveys.
Additionally, it is essential to ascertain potential risks. This aids in minimising future problems and developmental errors.
During business analysis, the developers gauge the product’s cost, profit, and sales feasibility. They then survey and compare the product with similar ones to meet customer demand. They consult case studies of similar market products to analyse risks and seek alternative solutions.
#4. Product development
Once initial steps are cleared, product ideas become concrete products. Thus, the R&D team could launch a prototype model of the product concept. The market sees the release of prototypes to assess consumer reach and demand satisfaction.
Market findings dictate the development and launch of the final product.
At this stage, the involvement of different departments is vital.
The marketing team develops strategies for product distribution. The finance team handles product costs and calculations. Lastly, the advertising team devises a plan for product promotion across platforms.
#5. Testing
The company launches a prototype to acquire customer feedback. This enables developers to test diverse strategies. These aspects encompass marketing, positioning, advertising, targeting, packaging, and financing.
The prototype’s target market serves as a source of customer feedback. Taking customer feedback into consideration. Feedback is then utilised to enhance the product further.
#6 Commercialisation
The product is brought to market after the test phase and feedback integration. Test marketing provides officials with a glimpse of the product’s real-world functionality.
Before the product hits the market, key decisions are made. This involves identifying the desired consumer base. Preparation of launch strategies is also done; after that, teams from various departments collaborate on the product.
Characteristics of a successful product development
There are common characteristics of successful product developments you can implement to increase the probability of product success.
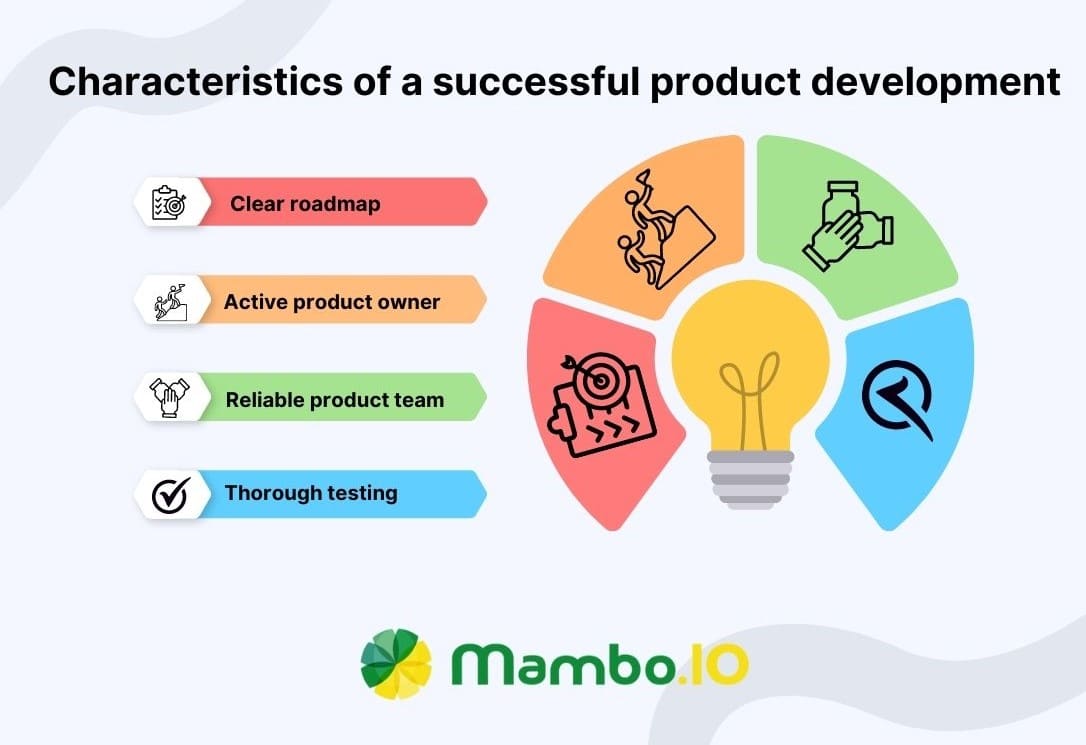
- A clear roadmap – Successfully designing a product is only the tip of the iceberg regarding product development. You must set a clear roadmap to attain your goals and objectives to succeed. Create a solid product roadmap that identifies your target market and price and defines your product.
- Has an active product owner – The product owner is the role in a product team responsible for the product’s outcome. A dynamic product owner is crucial to the success of product development. They are responsible for all the decisions from idea generation to product launch.
- Has a reliable product team – To achieve product development success, you need a team of experts that are dedicated to delivering high-quality products on time.
- Thorough testing – The main goal of product developers should be to develop a product that prioritises user needs. Testing your product with customers provides valuable feedback you can use to improve it in a way they will love.
Product design VS product development
Product design and development go hand in hand. They are both essential for new product marketing as they have overlapping functions.
Yet, they tackle unique challenges when creating a new product:
- Product design is about aesthetics, encompassing colour, contrast, and readability. The core of product development lies in ensuring functionality and usability.
- Product design creates sketches or prototypes to work from. However, precise technical drawings and specifications are a must in product development.
- Product design involves user testing or surveying. But, product development includes rigorous quality assurance and extensive digital prototyping.
- Product design conveys brand messaging, and product development optimises performance.
- Product design enables easy scalability for upgrades or customisation. Product development ensures higher production without compromising on quality.
- Unique skill sets are essential for both processes. Creative thinking is fundamental for designers. Developers rely on technical know-how and analytical capabilities.
Conclusion
Generally, the first stage is product design. It aids developers in grasping their creation’s alignment with customer use cases.
This insight enables the creation of a meticulous development strategy for their work. In essence, a well-designed product eases development.
Product developers and designers collaborate closely for the product’s final launch. It undergoes many life cycle stages to deliver the best product to customers.
Product design and development hold significance due to the prototypes crafted by designers. Testing takes place as the business uses these prototypes.
The product reaches the target audience, and their feedback is gathered for improvement. The end goal is to hold a prominent market standing.
If you want to increase engagement with your product design and development, our Mambo experts are excited to work with you. Book a demo now!
Download your free
“Gamification Guide”
Get your PDF now and start transforming your approach to digital engagement!
Latest Posts
Machine Learning In Finance: 12 Essential Applications
The impact of machine learning on finance is significant. Thanks to this technology, financial institutions are now equipped to make efficient decisions. Through the analysis of data sets, machine learning […]
How To Create Interactive Compliance Training For Bank Employees
Banking compliance training isn’t just another task. It’s the stage where everything else performs. Banks must navigate a myriad of regulations and laws. After all, this is a trust-driven, high-stakes […]
How Fintech Apps Are Using Gamification To Increase User Engagement
Discover how gamification in fintech is revolutionizing financial engagement, making banking fun & boosting user loyalty.





