The Importance Of A Product Design Portfolio And How To Create It
A Product Design Portfolio is what you use to display your design work. Your product design portfolio showcases your skills, experience, and success as a product designer.
Your product design portfolio can make you stand out, show your value, and express your unique design vision. It can also show how you design, solve problems, and deliver user-centric solutions.
Product managers will also benefit from it. It will help them make better products and work with designers and stakeholders.
In this article, you will learn how to show your skills and attract clients with product portfolio design. You will also learn the right elements for your presentations and projects.
Table of Contents
- Who counts as a product portfolio designer?
- What is the difference between UX designer and a product designer?
- How to create a product design portfolio
- Key elements of a successful product design portfolio
- Tips for presenting your portfolio
- How many projects to include and how to choose them
- Conclusion
- Machine Learning In Finance: 12 Essential Applications
- How To Create Interactive Compliance Training For Bank Employees
- How Fintech Apps Are Using Gamification To Increase User Engagement
- Top Gamification Companies for Employee & Customer Engagement
Who counts as a product portfolio designer?
A product portfolio designer designs products or services that solve problems for users and customers. Unlike graphic designers or UX designers, who concentrate on the product’s looks and functions, a product portfolio designer has a broader scope.
A product portfolio designer also considers a product’s business goals, user needs, market trends, and technical constraints.
The term “product portfolio designer” is relatively new and emerged from the intersection of user experience (UX) design and product management.
Product designers possess the necessary skills to excel in both and bear both responsibilities. They are the ideal bridges that find the “happy middle” between the users and the business.
What is the difference between UX designer and a product designer?
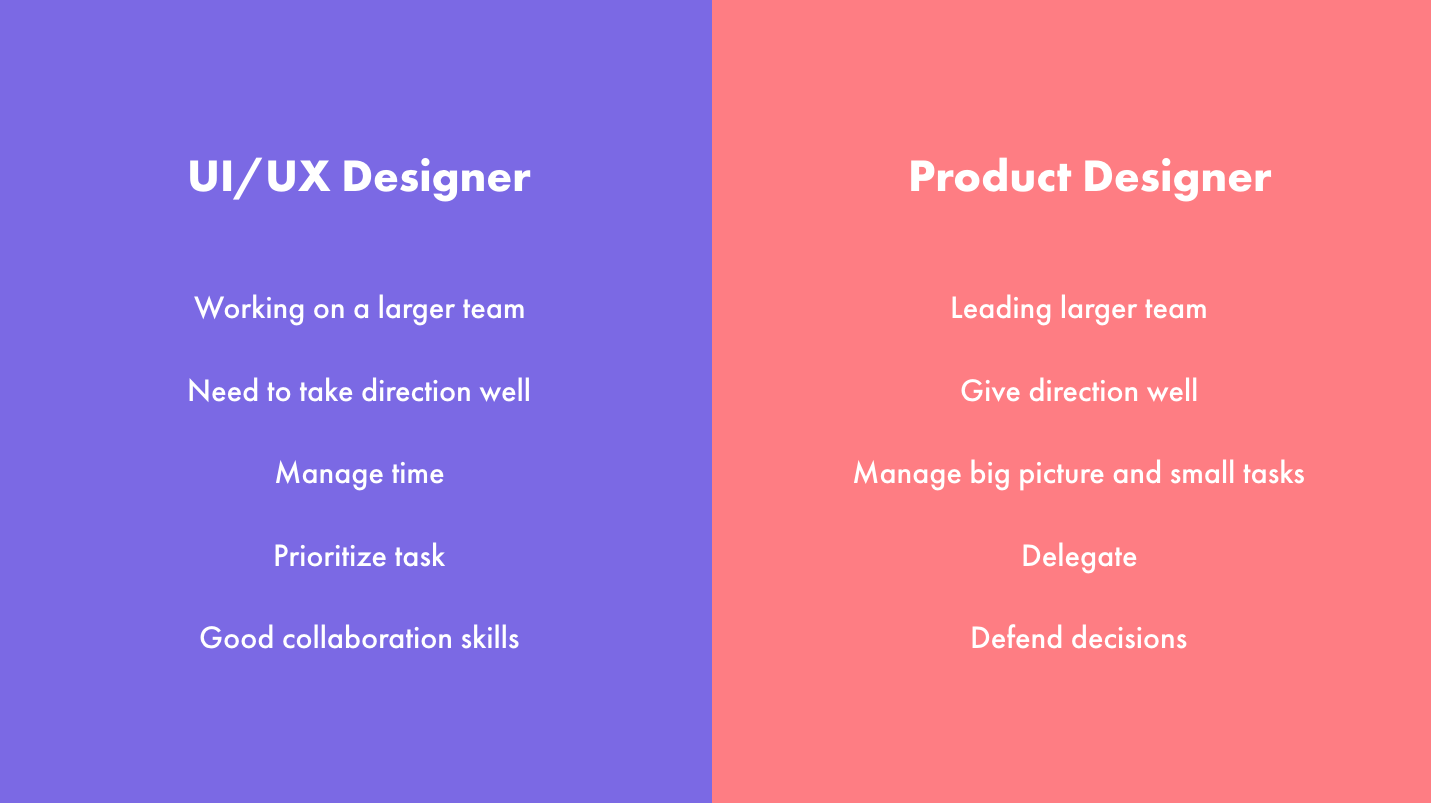
Designers are often pooled into one category. However, there are different specialities for each designer. Take a Product Designer and a UX Designer as examples. Both are seemingly related types of designers, yet they tend to do things differently.
UX designers are people who focus on designing the user experience of a product or service. They conduct user research, create user personas, and define user journeys.
Designing wireframes and prototypes for clients, conducting usability testing, and evaluating user feedback are tasks for a UX designer.
Designing the whole product or service from idea to launch is the role of a product designer. A product designer sets the product’s vision, strategy, and roadmap.
They also research the market and competition, test product concepts with users, and design user interfaces and interactions. They work with developers and engineers to evaluate product results and impacts.
Source: DesignerUp
Both roles share some skills and tasks and are responsible for making a human-centred design but differ in focus.
How to create a product design portfolio
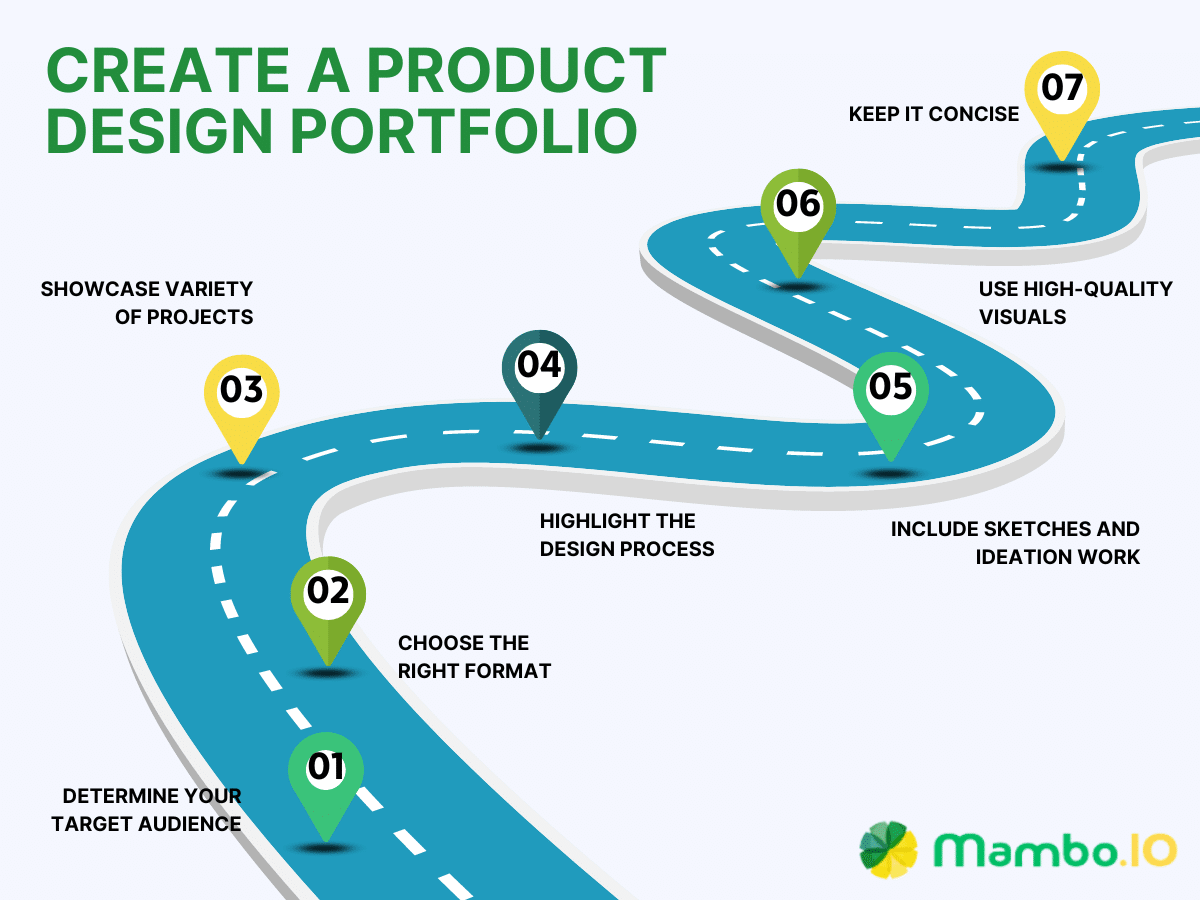
Making a product design portfolio can be hard but rewarding. Time, effort, creativity, and reflection are required. Here are steps to making a product design portfolio that shows your skills, passion projects, and achievements as a product designer.
#1. Determine your target audience
Knowledge of your target audience will be essential to creating a fantastic portfolio. You must find out and really get to know your potential clients.
It can either be companies or organisations that you want to work for or with. Understand their needs and expectations, and explore their preferences and pain points.
Tailor your portfolio to suit their needs and interests. Show skills, experience, achievements, values, etc., relevant to them. Avoid any mistakes or issues that might be hindrances sooner or later.
#2. Choose the right format
Your presentation is the ultimate statement of your intent. Choose the right format, which might give your presentation the edge that impresses your potential client.
There are varying options, each with pros and cons depending on your goals, preferences, and resources.
Some choices for the format of a product design portfolio are:
Online platforms
Online platforms like Behance, Dribble, and Medium let you make and host your portfolio online. They are handy, easy, and diverse but can also be restrictive, generic, and unreliable.
Source: Dribble
Websites
If you want to highlight your individuality, a portfolio website is excellent. A portfolio website lets you customise and create a place that is uniquely yours. Web Development tools such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, etc., are there to ensure you have a website that exactly suits you.
Source: Bashooka
PDFs
PDFs are certainly the most common format. They require the use of word processors or presentation software provided by the likes of Microsoft Office or Google Workspace. This format might be simple and inexpensive, but it may get stagnant, stale, and unappealing.

Source: WebTopic
Slides
Using slides as a format will give you a dynamic, engaging, and personal portfolio. You will use presentation software or services like Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides, Keynote, etc.
Restraint should be exercised, however, when using this format, as the end result might become distracting and cluttered.
Source: Microsoft
Videos
Using video editing software or services like Adobe Premiere Pro, After Effects, or iMovie is another great option. Immersing, interacting, and impressing with it is desirable, but facing difficulty, expense, and incompatibility is also unavoidable.
Source: Biteable
Your portfolio format will determine your preferences, target audience, project type, and resources. You can also mix different formats for different purposes or audiences. For example, you can use a portfolio website as your main portfolio and have a PDF, slide, or video version as a supplement.
#3. Showcase a variety of projects
The next step is to show different projects in your portfolio that show your skills, experience, and achievements. You should include projects that show your range, diversity, and versatility as a product designer.
You should also include projects that match your target audience’s needs, interests, business goals, challenges, etc.
Some factors to consider when choosing projects for your portfolio are:
Relevance
Choose projects relevant to the position, industry, domain, problem, and solution you are targeting. For example, if you are applying to an e-commerce company, you should include projects that involve designing e-commerce products.
Quality
Choose projects that are high-quality polished, and complete. Projects that are unfinished, low-quality, outdated, etc., should be avoided. For example, only show the parts done well or finished for an in-progress project.
Impact
Projects that positively impact users, customers, businesses, and society should be chosen. Show how you solved real-world user problems and delivered user-centric solutions.
For example, you should highlight in your portfolio a project that improved the conversion rate of an online store by 20%.
Diversity
Choose projects showing different products, services, platforms, devices, users, customers, and/or markets. Show how you can design for different contexts, scenarios, and situations.
#4. Highlight your design process
The next step is highlighting your design process for each project in your portfolio. Show how you design the project from idea to solution and how you involve users, stakeholders, and developers.
Use the five phases of design thinking: empathise, define, ideate, prototype, and test.
Explain and show what and why you did it in each phase. Show the deliverables or outcomes of each phase.
Show how you think and work as a product designer. Demonstrate your problem-solving skills, user empathy, creativity, collaboration, and attention to detail.
#5. Include sketches and ideation work
The next step is to add sketches and ideation work to your portfolio. Show the drawings or concepts you make in your design process’s ideation phase. Show how you try different ideas and solutions for a problem or opportunity.
Use pen and paper, digital tools, or physical materials. Add notes or comments. Show how you create and test ideas and solutions. Show your creativity, innovation, and experimentation skills.
#6. Use high-quality visuals
Using high-quality visuals in your portfolio is the next step. You use visuals, which are images or graphics, to present your work in your portfolio. Examples of visual presentations are screenshots, mockups, photos, videos, or animations.
Your target audience can be captivated and interested in visuals. They can also communicate your design vision and style effectively. The functionality and interactivity of your various digital products or services can also be showcased through visuals.
Tips on choosing high-quality visuals
Here are a few tips for choosing high-quality visuals for your portfolio:
- Select images that are clear and sharp.
- Pick colours, fonts, and icons that are consistent and fit your brand and design.
- Use realistic and relevant visuals that reflect the products or services you have designed.
- Show different aspects of your work by using different types of visuals. You can use static, dynamic, 2D, or 3D design.
- Explain or highlight essential details or features of your visuals by using captions, labels, annotations, etc.
- Use tools or services such as Figma Sketch, Adobe XD, InVision, Marvel, etc. to create or edit your visuals.
#7. Keep it concise
Your portfolio must be kept concise. Making the entire showcase brief yet still comprehensive and impactful can make it easier to understand and appreciate. Only essential information must be included, and irrelevant information for the target audience should be left out.
Following these tips will help you keep your portfolio concise:
- Use clear and simple language for your target audience.
- Use bullet points, lists, headings, and subheadings to organise and structure your information.
- Use short sentences, paragraphs, sections, etc., to simplify your information.
- Use relevant and meaningful keywords, phrases, and terms for your target audience.
- Use examples, statistics, quotes, and testimonials to support and illustrate your information.
- Use links, references, and sources for more information if needed.
Key elements of a successful product design portfolio
Now that you know how to create a great product design portfolio, let’s look at some key elements that make it successful. A successful product design portfolio impresses and persuades your target audience or potential clients to hire or work with you.
Here are some key elements that make a product design portfolio successful:
#1. Clear and concise project descriptions
A project summary in your portfolio is a clear and concise project description. The project’s name, type, goal, problem, solution, role, outcome, and other aspects are summarised in this part.
A clear project description enables your target audience to comprehend its purpose and why it is important. It will give them an understanding of your process and what you accomplished.
Tips on creating a clear and concise project description
A clear and concise project description should answer::
- Project’s name and type?
- The goals and problems of the project?
- Solution and role of the project.
- The project’s outcome and impact.
A clear and concise project description should also follow these tips:
- Use a catchy title and a subtitle or tagline.
- Use a paragraph or two with more details.
- Use relevant keywords, phrases, terms, etc.
- Utilise the numbers, percentages, metrics, etc.
Here is an example of creating a clear and concise project description:
Simon Pan is a product designer. His portfolio showcases his work on various projects, such as Uber Magic, Amazon Prime Music, and London by Bike. He explains each project’s challenges, goals, solutions, and outcomes in detail. He also shows his design process, deliverables, and impact.

Source: Simon Pan
#2. A strong visual hierarchy
A strong visual hierarchy is how you organise and present your visual design in your portfolio. It shows how you guide your target audience’s attention and interest. It also shows how you emphasise or prioritise some visuals over others.
A strong visual hierarchy helps your target audience see and understand the context of your work better. It also helps your target audience appreciate and remember your work better.
To create a strong visual hierarchy in your portfolio’s background, follow these principles:
Contrast
Create contrast between your visuals using different sizes, shapes, colours, fonts, backgrounds, etc. Contrast helps you create focal points or point out areas of interest. Contrast also helps you create balance or harmony.
Alignment
Use consistent and appropriate alignment for your visuals. Alignment helps you create order or structure in visual design. Alignment also helps you create clarity or readability.
Proximity
Use appropriate spacing or grouping for your visuals. Proximity helps you create relationships or connections between your visuals. Proximity also helps you create categories or sections.
Repetition
Use consistent and appropriate repetition for your visuals. Repetition helps you create consistency or coherence. Repetition also helps you create an identity or personal brand.
#3. A cohesive design aesthetic
A cohesive design aesthetic is your design style or personality in your various design portfolio examples. By using design elements, principles, and best practices, your portfolio examples will show your uniqueness, appeal, and professionalism.
Your target audience will recognise, remember, trust, and respect you as a product designer.
To create a cohesive design aesthetic in your portfolio, you should:
- Use colours to create mood, emotion, and emphasis.
- Use fonts to create hierarchy, emphasis, and clarity.
- Use icons to create meaning, navigation, and feedback.
- Use images to create context, impact, and emotion.
- Use design principles in your portfolio to create harmony, order, and structure.
- Use design best practices to create readability, usability, accessibility, etc., in your portfolio.
#4. Evidence of your design process and problem-solving skills
Your design process and problem-solving skills show your thinking and work as a product designer. They show your solution, your involvement in the design challenges, and your learning through the design journey.
Your target audience can value and assess your contribution to the project. They will also appreciate and compare your skills and abilities.
To demonstrate your problem solving skills, here are a few tips to show your design process in your portfolio:
- You should explain your process and objectives in each phase of your design process.
- Show the deliverables or outcomes of each phase.
- Highlight the challenges or uncertainties and how you solved or resolved them.
- Highlight the feedback or outcomes and how you learned or improved from them.
- Use storytelling techniques to make your design process and problem-solving skills engaging and memorable.
#5. Demonstrated ability to communicate effectively
Your effective communication skills show clear, concise, and confident communication. They also show your expression and understanding and help your target audience trust, respect, collaborate, and work with you.
To demonstrate your ability to communicate effectively:
- You should use clear and simple words for your intended audience.
- Choose clear and relevant visuals to support or illustrate your communication skills.
- Use natural and expressive gestures to enhance or emphasise your communication.
- Utilize listening skills to show your attention and interest in others’ communication.
- Use questioning skills to elicit or verify information from others’ communication.
- Use empathising skills to show your understanding and care for others’ communication.
Tips for presenting your portfolio
Presenting a portfolio is an effective way to showcase your work to your client. It can be an online, offline, live, recorded, solo, team, casual, or formal presentation.
Presenting your portfolio requires preparation, practice, confidence, and feedback. Here are some tips for presenting your portfolio effectively:
Tailor your portfolio to the position you are applying for
Research the company, project, role, etc., you want to work for or with. Understand their needs, expectations, preferences, and struggles. Choose the projects that best showcase your skills, achievements, values, and fit for the role. Make sure they are relevant, impressive, and error-free.
Practice presenting your portfolio
Practice your portfolio presentation in front of different audiences and settings. Use a mirror to help you practice. A camera, a friend, a colleague, or a mentor around you would be handy too.
Be prepared to discuss your design decisions and problem-solving process
Answer any questions or feedback from your target audience and explain your design choices and problem-solving methods.
You can demonstrate your confidence, knowledge, and ability by being prepared to discuss your design decisions, methods and problem-solving process.
Be open to feedback and critique
Listen to and appreciate any feedback or critique your target audience may give you. Respond to and act on any feedback or critique they may give you.
By being open to feedback and critique, you can show your art, humility, respect, curiosity, eagerness, adaptability, and flexibility.
How many projects to include and how to choose them
The sweet spot is what everybody is asking for. But choosing the best number and type of projects for their portfolio is for product designers to answer themselves.
You should include three to six projects, depending on their type, scope, quality, and impact. You should also consider your portfolio’s length, format, and medium. This will show your skills, experience, and achievements without overwhelming or tiring your target audience.
To choose projects, follow these criteria:
- They should be relevant to the position, industry, domain, problem, solution, etc.
- Choose projects that are high-quality, polished, and complete.
- Include projects that positively impact users, customers, businesses, and society.
- Showing different products, services, platforms, devices, users, customers, and markets.
- Choose projects that are recent or current.
Choosing projects based on these criteria helps you get noticed, shortlisted, interviewed, and hired. You can also show your target audience that you are interested, motivated, and qualified.
Conclusion
Product design portfolios show your design work, skills, experience, and achievements. It helps you stand out, impress, and communicate your design vision. Consider your target audience, format, projects, design process, visuals, and key elements to make it.
Mambo is a gamification platform that motivates users by incorporating exciting gaming elements into your systems.
Visit Mambo now, and don’t miss this opportunity to take your product design career to the next level!
Download your free
“Gamification Guide”
Get your PDF now and start transforming your approach to digital engagement!
Latest Posts
Machine Learning In Finance: 12 Essential Applications
The impact of machine learning on finance is significant. Thanks to this technology, financial institutions are now equipped to make efficient decisions. Through the analysis of data sets, machine learning […]
How To Create Interactive Compliance Training For Bank Employees
Banking compliance training isn’t just another task. It’s the stage where everything else performs. Banks must navigate a myriad of regulations and laws. After all, this is a trust-driven, high-stakes […]
How Fintech Apps Are Using Gamification To Increase User Engagement
Discover how gamification in fintech is revolutionizing financial engagement, making banking fun & boosting user loyalty.





